How to deal with high levels of iron and manganese in water sources
Water is a basic human need that cannot be replaced. In Indonesia, water refill businesses have become a popular solution to meet people's drinking water needs. However, the main challenge faced by water refill entrepreneurs is the quality of source water, which often contains high levels of iron and manganese. This article will take an in-depth look at how water refill businesses can address the issue of high levels of iron and manganese in source water, as well as other important aspects of the industry.
Introduction

The water refill business has become an inseparable phenomenon in Indonesian society. Its existence answers the need for safe, affordable, and easily accessible drinking water. However, despite its popularity, the industry faces major challenges when it comes to the quality of the source water used.
One of the major issues that often plague water refills is the quality of the water used.
One of the main problems often encountered is the high levels of iron and manganese in the source water. These two elements, while being naturally occurring minerals commonly found in groundwater, can pose a variety of problems if their concentrations exceed permissible limits. Iron and manganese can cause discoloration, taste, and odor to the water, as well as potentially damage water treatment equipment and infrastructure.
For water refillers, addressing these issues is not just about meeting water quality standards, but also about a moral responsibility to provide safe drinking water to consumers. They have an obligation to ensure that the water they produce is free from harmful contaminants and meets the health standards set by the government.
In this context, an understanding of this issue is important.
In this context, a deep understanding of water sources, treatment technologies, and industry best practices is critical. Water refillers need to have a comprehensive knowledge of various water treatment methods, including filtration, reverse osmosis, and disinfection, and how to apply them effectively to address iron and manganese issues.
In addition, they also need to have a comprehensive knowledge of the various water treatment methods, including filtration, reverse osmosis, and disinfection.
In addition, they should also understand the importance of system maintenance, regular water quality monitoring, and the implementation of strict sanitation practices. All of these are critical components in maintaining product quality and consumer confidence.
This article will explore the importance of system maintenance, regular water quality monitoring, and the implementation of strict sanitation practices.
This article will explore in depth the various important aspects of managing a water refill business, with a special focus on strategies to address high levels of iron and manganese in source water. We will discuss the latest technologies, industry best practices, and the challenges and opportunities that exist in this business.
Understanding the Iron and Manganese Problem in Source Water
Iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn) are two elements that are often found in groundwater in various parts of Indonesia. The presence of these two elements in high concentrations can cause various problems, both from an aesthetic and technical point of view in water treatment.
Iron, when oxidized, can cause water to have a reddish or brownish color, leave stains on clothes and sanitary equipment, and give water a metallic taste. Meanwhile, manganese can cause the water to take on a blackish color and impart an unpleasant taste.
In addition to aesthetic concerns, high concentrations of iron and manganese can also cause technical problems in water treatment systems. Both elements can precipitate and form scale on pipes, filters, and other equipment, reducing system efficiency and increasing maintenance costs.
To address these issues, entrepreneurs need to address these problems.
To address these issues, water refill entrepreneurs need to understand the characteristics of their source water and design an effective treatment system. This involves a series of steps, from the selection of the right water source to the application of appropriate treatment technologies.
Water Treatment Strategies to Remove Iron and Manganese
There are several methods that can be used to remove or reduce iron and manganese levels in water. The selection of the method depends on the characteristics of the source water, the level of contamination, and the scale of operation of the water refill business.
1. Aeration and Filtration
One of the most common methods is aeration followed by filtration. The aeration process involves adding oxygen to the water, which oxidizes dissolved iron and manganese into insoluble forms. These particles can then be removed through the filtration process.
Aeration systems can be either cascade aerators, where water is passed through a series of ladders to increase contact with air, or air diffusion systems, where air bubbles are injected into the water. After aeration, the water then passes through media filters such as sand or anthracite to remove iron and manganese particles that have oxidized.
2. Chemical Oxidation
For cases where iron and manganese levels are very high, chemical oxidation may be necessary. Chemicals such as chlorine, potassium permanganate, or ozone can be used to rapidly oxidize iron and manganese. This process is usually followed by filtration to remove the oxidized particles.
The use of the right chemical dosing pump is essential in this process to ensure accurate and consistent dosing. Dosing pumps from HydroPro, for example, can be a good choice for this application.
3. Filtration with Specialty Media
Several types of specialized filter media have been developed to remove iron and manganese. One of these is the Birm media from Clack, which is effective in removing dissolved iron from water. This medium works by catalyzing the iron oxidation reaction, allowing for efficient removal through filtration.
Another popular medium is manganese greensand, which is highly effective in removing both iron and manganese. Greensand works through ion exchange and oxidation processes, converting dissolved iron and manganese into filterable forms.
4. Reverse Osmosis (RO)
For more thorough water treatment, a reverse osmosis (RO) system can be an effective option. RO not only removes iron and manganese, but also a variety of other contaminants, including dissolved salts, bacteria, and viruses.
The RO system utilizes a semi-permeable membrane to remove iron and manganese.
RO systems use semi-permeable membranes to filter contaminants from water. For water refill applications, specialized RO membranes such as DuPont TAPTEC membranes can be a good choice, as they are designed specifically for filling stations or bottle refills.
Water Treatment System Design for Refill Business
Designing an effective water treatment system for a refill business requires a comprehensive approach. Here are some key components to consider:
1. Water Storage

An adequate water storage system is essential to ensure a consistent water supply. Storage tanks should be made of materials that are safe for drinking water and easy to clean. Wellmate's pressurized storage tanks can be a good choice for water systems.
2. Phased Filtration System
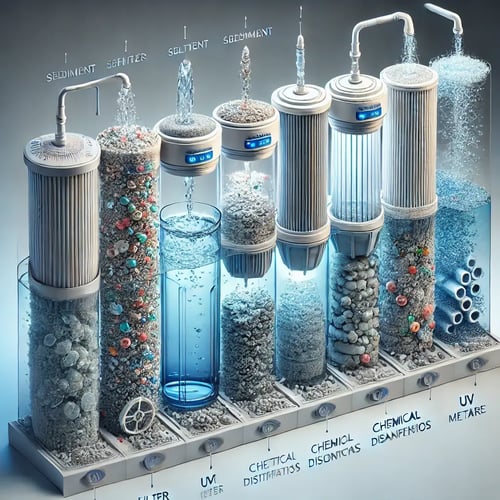

Staged filtration is required to remove different types of contaminants. It can start with a sediment filter to remove coarse particles, followed by an activated carbon filter to remove chlorine and organic matter. The NSF-certified Pentair Pentek filter cartridge can be a good choice for various water treatment applications.
Read more:
Understanding Hard Water: Definition, Types, and Uses
3. Reverse Osmosis System

For more thorough water treatment, an RO system is highly recommended. This involves the use of high-quality RO membranes, high-pressure pumps, and proper control systems. An energy-efficient Flint & Walling RO pump can be a good choice for an RO system.
4. Disinfection System
Disinfection is an important step to ensure the microbiological safety of water. UV and ozone systems are often used in the water refill industry. HydroPro's UV system can be an effective option for water disinfection.
5. Control and Monitoring System

Automated control systems and real-time water quality monitoring are essential to ensure efficient and consistent operations. This could involve the use of pH and conductivity sensors, as well as automated control systems for various treatment processes.
Best Practices in Operation and Maintenance
Running a successful water refill business is not only about having the right equipment, but also about implementing good operation and maintenance practices. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
1. Routine Water Quality Monitoring
Conduct regular water quality testing, both at the water source and in the final product. This includes testing for physical, chemical, and microbiological parameters. The use of Create pH and conductivity analyzers can help in real-time water quality monitoring.
2. Periodic Cleaning and Sanitization
Perform periodic cleaning and sanitizing of the entire system, including storage tanks, pipes, and treatment equipment. Use cleaning and sanitizing agents that are safe for drinking water.
3. Preventive Maintenance
Implement a preventive maintenance program for all equipment. This includes regular filter changes, sensor checks and calibrations, and pump and valve maintenance.
4. Employee Training
Ensure all employees are properly trained in system operations, sanitization procedures, and safety protocols. Training should include an understanding of the importance of water quality and how to handle issues that may arise.
5. Documentation and Recordkeeping
Maintain a good documentation system for all aspects of the operation, including water quality test results, maintenance records, and production logs. This is important not only for regulatory purposes but also for overall system performance monitoring.
Challenges and Opportunities in the Water Refill Industry

The water refill industry in Indonesia faces various challenges, but also offers exciting opportunities. Some of the key challenges include:
1. Strict Regulations
The Indonesian government is increasingly tightening regulations regarding drinking water quality. Water refill entrepreneurs must constantly update their knowledge on the latest standards and regulations.
2. Intense Competition
With so many players in the industry, competition is fierce. Entrepreneurs need to constantly innovate and improve their service quality to stay competitive.
3. Source Water Quality Fluctuations
Source water quality can fluctuate depending on the season and other environmental factors. This requires a flexible treatment system and the ability to customize the treatment process as needed.
4. Operating Costs
Electricity, chemicals, and maintenance costs can be a significant burden. Entrepreneurs need to find ways to optimize their operational efficiency.
However, behind these challenges, there are also exciting opportunities:
1. Increased Public Awareness
Public awareness of the importance of safe drinking water continues to increase. This opens up opportunities for entrepreneurs who can provide high-quality products.
2. Technological Innovation
Developments in water treatment technology open up opportunities to improve efficiency and product quality. Entrepreneurs who can adopt the latest technology will have a competitive advantage.
3. Product Diversification
There are opportunities for product diversification, for example by offering mineral water with added minerals or alkaline water.
4. Expansion to New Regions
There are still many areas in Indonesia that are not well served by the water refill industry, opening up opportunities for expansion.
Conclusion
The water refill business in Indonesia faces significant challenges, especially when it comes to addressing the high levels of iron and manganese in source water. However, with a good understanding of water treatment technologies, implementation of best practices in operations and maintenance, and a commitment to quality, entrepreneurs can overcome these challenges and even turn them into opportunities.
The key to success in this industry lies in overcoming these challenges.
The key to success in this industry lies in the ability to consistently provide safe, high-quality drinking water. This requires investment in the right technology, adequate employee training, and a commitment to continuous quality monitoring and improvement.
The use of technology such as RO systems is a key component to success in this industry.
The use of technologies such as RO systems, specialized media filters, and UV disinfection systems can be very helpful in addressing iron and manganese issues. However, it is important to remember that there is no "one-size-fits-all" solution. Each water refill business needs to design a treatment system that fits the characteristics of their source water and the specific needs of their operation.
In addition, entrepreneurs also need to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in water treatment technology and industry regulations. This will help them not only in meeting the set quality standards, but also in optimizing their operations and providing added value to customers.
Finally, it is important to design a treatment system that is suitable for their source water characteristics and the specific needs of their operations.
Finally, it is important to remember that the water refill business is not just about providing a product, but also about providing an important service to society. With a focus on quality, safety, and customer satisfaction, water refill entrepreneurs can build a business that is not only profitable, but also makes a positive contribution to the health and well-being of Indonesians.
Q&A About Water Refill Business
Q1: How do I know if the source water contains high levels of iron and manganese?
A1: To know the level of iron and manganese in the source water, you need to do laboratory testing. Visual signs such as reddish or blackish colored water, as well as deposits or stains on equipment, can be early indications. However, laboratory testing is still necessary to get accurate results.
Q2: Is a Reverse Osmosis (RO) system always necessary in a water refill business?
A2: Not always, depending on the source water quality and the standards to be achieved. However, RO systems are highly effective in removing a wide range of contaminants, including iron and manganese, and provide high water quality assurance. For businesses looking to offer premium products or facing complex water quality issues, an RO system can be a worthwhile investment.
Q3: How often should water quality monitoring be done in a refill business?
A3: Water quality monitoring should be done regularly. For basic parameters such as pH, TDS, and turbidity, monitoring can be done daily. For more comprehensive microbiological and chemical analysis, it should be done at least once a month or according to local regulations. In addition, additional monitoring may be required if there are significant changes to the source water quality or after performing major maintenance on the treatment system.
References
1. Byrne, W. "Reverse Osmosis: A Practical Guide for Industrial Users." (2nd Edition). Tall Oaks Publishing, 2002.
2. Spellman, F.R. "Handbook of Water and Wastewater Treatment Plant Operations." CRC Press, 2003.
3. World Health Organization. "Guidelines for Drinking-water Quality." (4th Edition). WHO Press, 2011.
4. Binnie, C. and Kimber, M. "Basic Water Treatment." (5th Edition). ICE Publishing, 2013.
5. American Water Works Association. "Water Quality and Treatment: A Handbook of Community Water Supplies." McGraw-Hill, 1999.

.png?width=50&height=50&name=Logo_Watermart_Perkasa-removebg-preview%20(1).png)


